API 7: Pruning
We usually use pruning to make neural networks sparser hence more efficient and more interpretable. KANs provide two ways of pruning: automatic pruning, and manual pruning.
Pruning nodes
from kan import *
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(device)
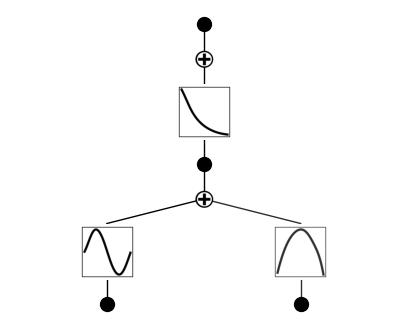
# create a KAN: 2D inputs, 1D output, and 5 hidden neurons. cubic spline (k=3), 5 grid intervals (grid=5).
model = KAN(width=[2,5,1], grid=5, k=3, seed=1, device=device)
# create dataset f(x,y) = exp(sin(pi*x)+y^2)
f = lambda x: torch.exp(torch.sin(torch.pi*x[:,[0]]) + x[:,[1]]**2)
dataset = create_dataset(f, n_var=2, device=device)
dataset['train_input'].shape, dataset['train_label'].shape
# train the model
model.fit(dataset, opt="LBFGS", steps=20, lamb=0.01);
model(dataset['train_input'])
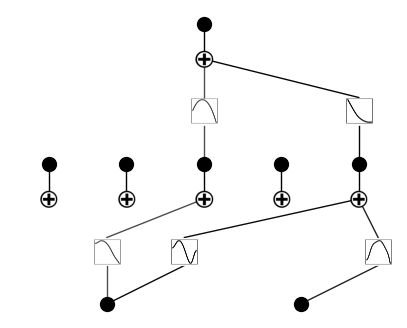
model.plot()
cuda
checkpoint directory created: ./model
saving model version 0.0
| train_loss: 3.46e-02 | test_loss: 3.46e-02 | reg: 4.91e+00 | : 100%|█| 20/20 [00:05<00:00, 3.36it
saving model version 0.1
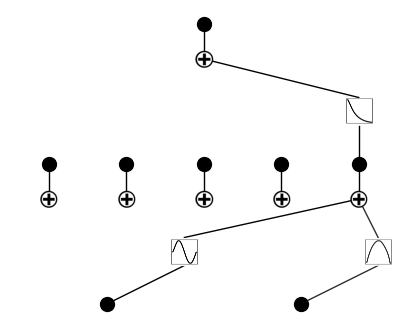
mode = 'auto'
if mode == 'auto':
# automatic
model = model.prune_node(threshold=1e-2) # by default the threshold is 1e-2
model.plot()
elif mode == 'manual':
# manual
model = model.prune_node(active_neurons_id=[[0]])
saving model version 0.2
Pruning Edges
from kan import *
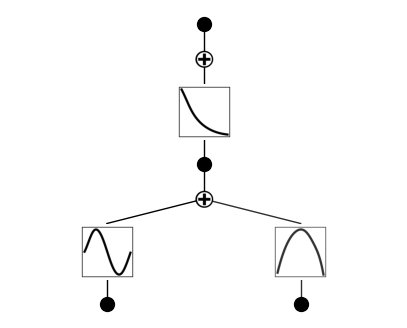
# create a KAN: 2D inputs, 1D output, and 5 hidden neurons. cubic spline (k=3), 5 grid intervals (grid=5).
model = KAN(width=[2,5,1], grid=5, k=3, seed=1, device=device)
# create dataset f(x,y) = exp(sin(pi*x)+y^2)
f = lambda x: torch.exp(torch.sin(torch.pi*x[:,[0]]) + x[:,[1]]**2)
dataset = create_dataset(f, n_var=2, device=device)
dataset['train_input'].shape, dataset['train_label'].shape
# train the model
model.fit(dataset, opt="LBFGS", steps=6, lamb=0.01);
model(dataset['train_input'])
model.plot()
checkpoint directory created: ./model
saving model version 0.0
| train_loss: 7.84e-02 | test_loss: 7.80e-02 | reg: 7.26e+00 | : 100%|█| 6/6 [00:01<00:00, 3.72it/s
saving model version 0.1
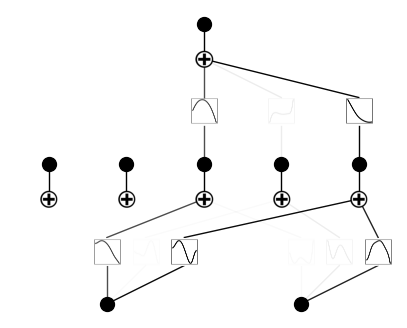
model.prune_edge()
saving model version 0.2
model.plot()
Prune nodes and edges together
just use model.prune()
from kan import *
# create a KAN: 2D inputs, 1D output, and 5 hidden neurons. cubic spline (k=3), 5 grid intervals (grid=5).
model = KAN(width=[2,5,1], grid=5, k=3, seed=1, device=device)
# create dataset f(x,y) = exp(sin(pi*x)+y^2)
f = lambda x: torch.exp(torch.sin(torch.pi*x[:,[0]]) + x[:,[1]]**2)
dataset = create_dataset(f, n_var=2, device=device)
dataset['train_input'].shape, dataset['train_label'].shape
# train the model
model.fit(dataset, opt="LBFGS", steps=20, lamb=0.01);
model(dataset['train_input'])
model.plot()
checkpoint directory created: ./model
saving model version 0.0
| train_loss: 3.46e-02 | test_loss: 3.46e-02 | reg: 4.91e+00 | : 100%|█| 20/20 [00:05<00:00, 3.70it
saving model version 0.1
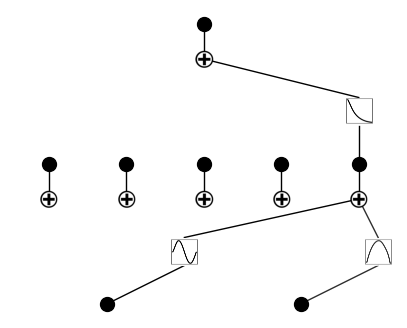
model = model.prune()
model.plot()
saving model version 0.2